通讯作者简介 王国强,男, 1990年生, 2020年毕业于中山大学地球科学与工程学院,获博士学位,现为山西师范大学地理科学学院教师,主要从事矿床勘查和纳米地球科学研究。 E-mail: wangguoqiang@sxnu.edu.cn。
第一作者简介 刘睿,男, 1990年生, 2017年毕业于中国科学院广州地球化学研究,获博士学位,现为山东理工大学资源与环境工程学院副教授,主要从事纳米地球科学研究。 E-mail: liurui@sdut.edu.cn。
至少一维尺度上小于 100 nm的矿物都属于纳米矿物的范畴,自然界中除了大量的人造纳米矿物之外,天然的纳米矿物分布也很广泛。随着透射电子显微镜( TEM)技术在地球科学中的应用,大量的天然纳米矿物在地壳表层和内部被发现。尤其是在矿田区域,与矿体相关的纳米矿物在各种介质中被发现,并且这些纳米矿物在矿床的研究中有着独特的作用。堆积型铝土矿床储量大,是铝土矿的重要来源。在堆积型铝土矿床中发育有大量的纳米矿物,矿石矿物也以纳米级晶体分布于矿床中,并且在纳米尺度上表现出结构和成分的变化,这些纳米矿物以及结构、成分的变化记录了铝土矿成矿过程的物理化学信息,为探究铝土矿的成因提供了独特的窗口。该综述总结了纳米矿物在研究堆积型铝土矿床中的优势,为研究堆积型铝土矿床的提供了新方法,为认识堆积型铝土矿的成因提供了新角度。
About the corresponding author Wang Guo-Qiang,born in 1990,obtained his Ph.D. degree from School of Earth Sciences and Engineering,Sun Yat-sen University in 2020. Now he is a teacher in Geography Science Institute,Shanxi Normal University,and is mainly engaged in mineral exploration and nanogeoscience. E-mail: wangguoqiang@sxnu.edu.cn.
About the first author Liu Rui,born in 1990,obtained his Ph.D. degree from Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2017. Now he is an associate professor in School of Resources and Environmental Engineering,Shandong University of Technology,and is mainly engaged in nanogeoscience. E-mail: liurui@sdut.edu.cn.
Nanomineral is the mineral that is less than 100 nm at least one dimension. Aside from the man-made nanominerals,there is a large number of natural nanominerals. With the increasing application of transmission electron microscopy(TEM)in earth science,a large number of natural nanominerals have been discovered in the surface and interior of the Earth. Especially in ore deposit region,nanominerals related to ore bodies are found in various media,and these nanominerals play a unique role in the research of ore deposits. The stacked bauxite deposit is an important source of bauxite because of its large reserve. There are a large number of nanominerals distributed in stacked bauxite deposit,and these ore nanominerals distributed in the deposit in the form of nanocrystals. In addition,the ore minerals in stacked bauxite deposit display changes of the structure and composition in nanoscale. The nanominerals as well as the changes of structure and composition in nanoscale can record the physical and chemical information of bauxite mineralization process,providing a unique window to explore the genesis of the stacked bauxite deposit. This review summarizes the advantages of nanominerals in the research on the stacked bauxite deposit,providing a new method and a new perspective for the understanding of the genesis of bauxite deposit.
纳米矿物是指在三维尺度至少有一维小于100 nm的矿物(图 1)。目前对纳米尺度的矿物学研究方法主要包括HR-SEM、TEM、FIB、nanoSIMS、AFM/STM和计算机模拟等(Reich et al., 2011)。纳米矿物由于其尺度效应, 在化学特性、力学特征、电学和磁学特征上均表现出与宏观矿物不同的特征(Hochella et al., 2008)。纳米矿物在自然界主要有2类: 天然纳米矿物和人造纳米矿物(包括人类有意和无意产生的)。其中人类有意合成的纳米矿物在成分上比较单一、形貌上比较规则, 而天然纳米矿物在成分上比较复杂、形貌多呈不规则状。随着纳米科学的发展, 越来越多的天然纳米矿物在自然界中被发现。天然纳米矿物的成因涉及到自然界中的各种物理化学过程, 包括溶解、沉淀、相变、燃烧、生物矿化等。纳米矿物由于其独特的物理化学性质, 已经表现出独特的地球化学功能和意义。例如, 纳米矿物由于其极小的尺寸极易被携带发生迁移(曹建劲, 2009), 因而也是成矿元素地球化学迁移的重要方式。
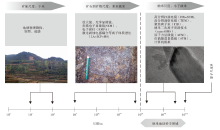 | 图 1 矿床学研究的不同尺度(据Reich et al., 2011; 修改)Fig.1 Dimensional scale of ore deposits research(modified from Reich et al., 2011) |
天然纳米矿物赋存于各种地质体中, 在矿床学领域, 过去一些不能解释的成矿机制、地质现象以及金属元素的存在形式等, 从纳米矿物的角度得到了较好的解释(琚宜文等, 2016; 王焰新和田熙科, 2016)。同时, 矿物是成矿过程的重要产物, 矿物内部纳米微粒可以提供更加直观和更加丰富的关于成矿过程的信息(曹建劲, 2009)。例如, 形成浅成金矿床的流体仅能够溶解10-9级别的金含量, 而这样低的金含量无法形成具有经济价值的矿床(Reich et al., 2006)。但是, 许多学者在卡林型金矿床的黄铁矿内部发现了含金纳米矿物和自然金纳米矿物(Ciobanu et al., 2011, 2012; Deditius et al., 2011; Pač evski et al., 2012; Fougerouse et al., 2016), 通过对这些纳米微粒的特征研究得出, 含金纳米微粒(或自然金纳米微粒)在黄铁矿中有很高的溶解度, 解释了金在形成浅成金矿过程中赋存形式的问题。大量的研究表明, 矿床中的与成矿物质有关的纳微米矿物种类丰富, 与矿床的成矿物质关系紧密, 有的成矿物质甚至直接以纳米微粒的形式出现在矿床中(纳米金、纳米银、纳米铅、纳米锌等)(图 2)。Deditius等(2011)和Hough等(2011)通过对矿床中纳微米矿物的特征探讨了成矿物质的赋存形式。Koneev等(2010)、Fougerouse等(2016)利用纳微米矿物的大小、分布状态阐明了寄主矿物和成矿物质的成因。Reich等(2006)、Pač evski等(2012)等利用纳微米矿物的特征和其他矿物的成分特征反映矿物经历的热事件。Sun和Xia(2002)等通过实验模拟得出纳微米矿物可以反映矿物形成时的物理化学条件。Gao等(2019)通过对钒钛磁铁矿床中的纳微米矿物进行研究, 并对磁铁矿的形成条件进行相平衡分析, 最终得出其形成过程。
 | 图 2 矿床中发现的各种金属纳米微粒 a— 广东长坑金矿床中的纳米金微粒(Cao, 2009); b— 内蒙古维拉斯托锌铜银多金属矿床中的纳米银微粒(Yi et al., 2019); c— 内蒙古石匠山区铅锌多金属矿矿床中的纳米锌微粒(Hu and Cao, 2019); d— 内蒙古石匠山区铅锌多金属矿矿床中的纳米铅微粒(Hu and Cao, 2019)Fig.2 Different kinds of metal nanoparticles found in ore deposits |
此外, 朱笑青和章振根(1996)、姜泽春等(1999)、傅宇虹等(2018)通过实验模拟得出, 许多颗粒较大的矿物对纳米矿物具有很强的吸附作用, 纳米矿物可在其他矿物表面大量地富集、迁移、成矿。曹建劲(2009)在对隐伏金属矿床地表和深部介质中的含矿纳米矿物进行研究, 并对金属纳米矿物的形成、迁移和找矿勘探意义进行分析探讨。由此可见, 纳米矿物在矿床学的研究中具有独特的作用, 对纳米矿物的研究在成矿过程和找矿勘探等方面都有很好的应用前景。
铝土矿是在潮湿的热带— 亚热带气候条下, 由地表风化和交代淋滤作用形成的富含Al、Fe和Ti的氢氧化物和氧化物(Bá rdossy, 1982; Bá rdossy and Aleva, 1990; D'Argenio and Mindszenty, 1995; Calagari and Abedini, 2007; Deng et al., 2010)。铝土矿的分类比较复杂, 目前应用比较广泛的分类为红土型铝土矿和喀斯特型(包括沉积型和堆积型)铝土矿(Bá rdossy, 1982; 杨俊波, 2005; Laskou and Economou-Eliopoulos, 2007; Deng et al., 2010)。堆积型铝土矿(萨伦托型)是铝土矿床的重要类型, 其矿床储量通常为大型— 超大型, 品位中等(王庆飞等, 2012)。该类型铝土矿床多产于含铝量较低的碳酸盐岩不整合面(侵蚀面)上(Bá rdossy and Aleva, 1990; D'Argenio and Mindszenty, 1995)。矿床所处的地貌多为岩溶洼地、坡地。已有的研究表明, 堆积型铝土矿床的成矿物质具有异源性, 在成矿过程中成矿物质经历了风化和搬运作用, 并在适宜的地质环境中沉积形成早期铝土矿层, 铝土矿层经过淋滤作用使成矿元素进一步富集(Valeton et al., 1987; 王泽中, 1997; 刘平, 1999; 李新, 2008; 韦胜永等, 2009)。
目前, 对于堆积型铝土矿床的矿床成因研究已经做了许多工作, 取得了一些成果。例如刘长龄和覃志安(1990)提出堆积型铝土矿的成矿母岩在物理和化学风化作用下形成含铝的胶体态物质, 成矿物质则以碎屑胶体混合形式进行迁移沉积, 淋滤过程中成矿元素在生物的作用下富集成矿; 廖士范和梁同荣(1991)认为堆积型铝土矿床的成矿母岩在风化作用下形成赋含铝土矿物的风化壳, 成矿物质以黏土矿物的形式进行迁移就位, 后期的淋滤作用对成矿的影响比较微弱; Ö ztü rk等(2002)提出堆积型铝土矿床的成矿物质从成矿母岩的风化壳中以细碎屑态被搬运至凹坑和洼地富集, 在淋滤过程中早期铝土矿中的其他元素(如Si和Mn)以离子形式被喀斯特排水系统迁移带走, 进而使成矿元素富集; Liu等(2010)则认为堆积型铝土矿成矿物质以含铝土壤的形式进行迁移、堆积, 在淋滤阶段成矿元素以离子化合物的形式结晶析出, 富集成矿。上述的研究表明堆积型铝土矿床总体的成矿过程已经基本查明, 但是对成矿物质在风化和搬运过程中的赋存形态并未取得一致的认识。同时, 对铝土矿在淋滤过程中成矿元素的富集机制也存在争论(廖士范和梁同荣, 1991; Ö ztü rk et al., 2002; 叶霖等, 2008; 刘幼平等, 2010)。
前人对于堆积型铝土矿的研究主要基于沉积学、 矿物学和地球化学的方法(侯正洪和李启津, 1985; 陈廷臻和武耀诚, 1986; 吕夏, 1988; 刘长龄和覃志安, 1990; 肖金凯等, 1994; 张玉学等, 1999; 杨军臣等, 2004; 鲁方康等, 2009; 杜远生等, 2014; Yu et al., 2014)。 例如通过对铝土矿沉积剖面的研究得出铝土矿的成矿环境(苏熠, 1985), 利用光学显微镜、 热差/热重分析(DTA/TG)、 X-射线衍射(XRD)、 红外光谱(FTIR)、 电子扫描显微镜(SEM)等仪器对铝土矿中的矿物组合以及结构进行研究(杨冠群和廖士范, 1986; 李普涛和张起钻, 2008; Dani, 2011), 利用X荧光光谱仪和等离子质谱仪对铝土矿中主量和微量元素进行测定(陈履安, 1996; 陈代演和王华, 1997; Mongelli and Acquafredda, 1999; Calagari and Abedini, 2007; Yang et al., 2019)。 矿石中同位素组成在堆积型铝土矿床的研究中应用也比较广泛, 例如利用硫化物32S/34S值特征分析铝土矿的形成环境(龙永珍, 2003), 利用氢氧同位素δ 18O和δ D对铝土矿的来源进行示踪(程东等, 2001)。 目前, 利用Rb-Sr、 40Ar-39Ar、 碎屑锆石U-Pb、 Hf等放射性同位素进行铝土矿矿床成因的研究也越来越普遍(刘巽锋等, 1990; 刘平, 1999; 赵社生等, 2001; 王银喜等, 2003; 林最近, 2007)。 此外, 古生物和古地磁的测定也在探讨铝土矿形成的古地理环境、 古气候以及成矿作用中发挥着一定的作用(施和生等, 1989; 莫江平, 1991; 吴国炎, 1997)。 近年来, 矿物微区的地球化学分析越来越多地应用于堆积型铝土矿矿床的研究中, 例如李(2017)通过对豫西铝土矿中金红石的激光探针(LA-ICP-MS)分析得出该地区铝土矿的成矿物质来源; 张亚男等(2013)对黔北务正道地区铝土矿中的鲕粒进行了微区(EPMA和LA-ICP-MS)地球化学特征研究, 反演了该地区铝土矿的形成过程及形成环境。
对于堆积型铝土矿床, 其成矿物质主要是风化作用的产物(Bá rdossy, 1982; Bá rdossy and Aleva, 1990), 而风化作用是天然纳米矿物微粒的重要成因(Chen et al., 2010)。在风化过程中, 被风化矿物表面可以形成大量的纳米矿物微粒(Griffin et al., 2018)。这些纳米矿物微粒可以长时间赋存于被风化矿物表面或者被迁移到其他地方保存下来(Schindler and Hochella, 2015; Schindler et al., 2019)。此外, 堆积型铝土矿床中的矿石矿物本身为极细小的晶体(纳米级)(Gamaletsos et al., 2017), 矿石由纳米级矿石矿物聚集形成(图 3)。因此, 铝土矿床本身就是一个天然纳米矿物微粒储库, 含有丰富的纳米矿物微粒, 利用纳米矿物微粒研究铝土矿床成矿物质的富集过程具有天然的优势。同时, 堆积型铝土矿床在形成过程中经历了长期的风化和淋滤作用, 原生铝土矿层中会有大量的元素淋滤流失, 例如S、P、Ca、Mg、Sr、Rb等(王庆飞等, 2012), 这样对于利用传统的地球化学方法研究成矿物质的富集过程具有很大的挑战。相反, 纳米矿物微粒则可以在长期的风化和搬运过程中保存下来。同时, 矿物的形成过程都会经历纳米矿物微粒阶段(杨毅等, 2018)。因此, 纳米矿物微粒为直接和准确地研究堆积型铝土矿床风化和迁移过程中成矿物质的赋存形态提供了有利条件。在此基础上可以通过对比铝土矿形成过程中不同阶段的纳米物质组成和特征, 用以分析纳米矿物在形成过程中的迁移和富集过程。
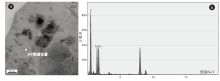 | 图 3 广西靖西特大型堆积铝土矿床中的纳米级矿石矿物 a— TEM形貌图; b— EDS能谱图Fig.3 Nanoscale ore minerals in Jingxi super large stacked bauxite deposit in Guangxi |
此外, 许多矿物(如硅酸盐矿物、铁钛氧化物、硫化物等)内部也含有大量的纳米矿物微粒(Filimonova and Trubkin, 2008; Koneev et al., 2010; Fougerouse et al., 2016), 由于寄主矿物的保护作用, 这些纳米矿物微粒通常保留有丰富的关于成矿物质的信息(Deditius et al., 2011; Hough et al., 2011; Ciobanu et al., 2011, 2012; Liu et al., 2020)。并且在堆积型铝土矿床的矿体中, 矿物常发育鲕状结构(刘长龄和覃志安, 1990) (图 4), 鲕状结构也是纳米矿物微粒赋存的理想场所。同时, 鲕状矿物不同圈层中的纳米矿物微粒可以记录下淋滤过程中元素迁移的物理化学条件(Schindler and Hochella, 2015; Schindler et al., 2019), 并且不同圈层中的纳米矿物微粒的结构和化学成分不同, 通过对比不同圈层中的纳米矿物微粒特征也可以反演元素的迁移过程, 这为研究堆积型铝土矿床成矿元素的富集和优化过程提供了便利。
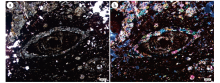 | 图 4 广西靖西特大型堆积铝土矿床中的鲕状结构 a— 单偏光照片; b— 正交偏光照片Fig.4 Olitic texture in Jingxi super large stacked bauxite deposit in Guangxi |
最后, 不论是成矿母岩的风化壳, 还是铝土矿床的矿石都表现为粉末状或疏松的块状, 这样的岩石和矿石构造便于原生纳米矿物微粒的提取和研究, 避免了由于人为对岩石和矿石的破碎而产生纳米矿物微粒。因此, 纳米矿物微粒是研究堆积型铝土矿床的良好手段。
纳米矿物学作为一门年轻的学科, 在矿床学研究中还处于起步阶段。纳米矿物本身具有特殊的理化性质以及独特的地球化学功能, 其在矿床成因研究的前景已经初步显现, 但是仍有许多方面的内容需要进一步探究, 例如纳米矿物在大型— 超大型矿床形成过程中的作用, 纳米矿物是否会对寄主矿物元素分布、同位素的组成造成影响, 进而影响地球化学的分析结果等等。
由于堆积型铝土矿床可以与纳米矿物学较好地结合, 应用纳米矿物可以从全新的角度去解决该类型矿床成因方面的问题。堆积型铝土矿床不仅成矿物质多为纳米矿物, 在风化、搬运和沉积过程中也会产生大量的其他类别的纳米矿物, 如棒状金红石纳米矿物、含铁纳米矿物等, 这些特殊的纳米矿物对于限定堆积型铝土矿床形成的物理化学条件也具有独特的作用。因此, 纳米矿物在堆积型铝土矿床的研究中具有较好的前景, 可为该类型矿床的研究提供新思路和新方法。
(责任编辑 李新坡; 英文审校 徐 杰)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|

