中国东部陆架边缘海发育多个全新世泥质区,是研究古海洋和古气候的理想区域。本研究从现代沉积过程和全新世沉积记录的视角,对山东半岛近岸泥质区的前人研究结果进行总结梳理,为后续相关研究提供参考。山东半岛近岸泥质区位于山东半岛沿岸,主要是来自黄河的沉积物在沿岸流、上升流、潮汐等相互作用下沉积而成,呈现独特的“ Ω”形沉积模式。山东半岛近岸泥质区形成于全新世,物质来源主要是黄河,近岸侵蚀和当地小河流也贡献一定的物质来源。山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成和演化与古海洋条件、海平面升降、内陆古气候演变等多种因素有关,蕴藏着丰富的环境演化信息。山东半岛近岸泥质区沉积能够快速记录东亚季风的演变,其较高的沉积速率为研究黄河流域的古气候和古生态演化提供高分辨率的材料,可为预测未来全球变化背景下黄河流域的发展趋势提供参考。虽然前人对现代沉积过程进行了大量工作,但仍需加强现代观测和数值模拟等方面的工作,为更好地重建研究区的沉积动力过程提供数据和理论支撑。此外,该区在长时间尺度上的沉积物和有机质的沉积过程对古海洋和古气候的响应机制也亟待开展研究。
About the first author: Gu Yu,born in 1997,a master degree candidate of geology in Ocean University of China, is mainly engaged in marine sedimentology. E-mail: guyu5129@stu.ouc.edu.cn.
第一作者简介:谷玉,女,1997年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为海洋沉积学。E-mail: guyu5129@stu.ouc.edu.cn。
The Holocene mud areas on the eastern continental shelf of China are an ideal area for studying paleoceanography and paleoclimate. From the perspective of modern sedimentary processes and Holocene sedimentary records,previous research results of the Holocene mud area off Shandong Peninsula are summarized to provide references for further studies. The mud area off Shandong Peninsula is located along the coast of Shandong Peninsula. It is mainly formed by the sediment from the Yellow River and deposited under the interaction of coastal,upwelling and tide currents,exhibiting a unique “Ω” shape. The mud area off Shandong Peninsula was formed by the last deglacial transgression in the Holocene. The Yellow River sediments are thought to be the main source of the mud area,while the nearshore erosion and local small rivers along the Shandong Peninsula coast also contributed sediments to the mud area. The formation and evolution of mud area record rich environmental information and are related to multi-factors,such as paleoceanography,sea-level changes and inland paleoclimatic evolution. The sedimentation of the mud area off Shandong Peninsula can respond to the evolution of East Asian Monsoon rapidly,and its high sedimentation rate can provide high resolution archive for the evolution of paleoclimate in the Yellow River Basin,which provide references for predicting the Yellow River Basin evolution under global climatic changes in future. Although a great deal of work has been done on modern sedimentary processes,modern observation and numerical simulation are still needed to provide data and theoretical support for better reconstruction of sedimentary dynamic processes in the study area. In addition,the response of the depositional processes of clastic sediment and organic matter to the paleoceanography and paleoclimate in the long-time scale need to be better understood.
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID): 
在全球源-汇系统中, 细粒泥质沉积(黏土和粉砂粒级)扮演着重要的角色。细粒泥质沉积作为有机质的主要载体, 是重要的碳储库, 是构成全球碳循环的重要组成部分(Oberle et al., 2014)。此外, 细粒泥质沉积物中普遍存在浅层天然气(Fleischer et al., 2001; Chen et al., 2020), 同时是页岩气和页岩油等非传统油气资源的载体(Li et al., 2020; 卢斌等, 2021), 对油气远景预测与勘探具有重要意义。内陆架是泥质沉积的重要场所, 在不同沉积环境下会形成不同类型的泥质沉积中心, Hanebuth等(2015)根据表层沉积物分布以及内部几何形状, 将泥质沉积中心划分为8种类型: 前三角洲、水下三角洲、泥质斑块、席状泥质体、泥质带、浅水等深流泥质体、泥质捕获体、泥质楔。Porz等(2021)提出泥质沉积中心发育具有3种范式: (1)连续供给, 与稳定的沉积物供给和相对平静条件下的半深海沉积相伴; (2)连续的重悬沉积循环, 其中泥质沉积中心部分区域在最终埋藏之前要经历多个再悬浮、再沉积和再改造的循环; (3)周期性的沉积和侵蚀, 极端事件(如洪水和风暴)主导着长期的总沉积物通量。
全新世以来, 中国东部边缘陆架海发育了多个不同类型的泥质区(高抒, 2013; 石学法等, 2021), 自北向南分别为渤海中部泥质区(刘建国等, 2007)、山东半岛近岸泥质区(Liu et al., 2004; Yang and Liu, 2007)、南黄海中部泥质区(胡邦琦等, 2012; Li et al., 2014)、南黄海东部泥质区(刘健等, 2003)、苏北沿岸老黄河口泥质区(朱纯等, 2005)、东海外陆架济州岛西南泥质区(向荣等, 2005)、长江口泥质区(郭志刚等, 2000; Yao et al., 2014)以及位于东海内陆架的浙闽沿岸泥质区(Liu et al., 2006, 2018a; Xu et al., 2012; 李安春和张凯棣, 2020)。这些泥质区的沉积记录可以很好地指示全新世以来古气候和古海洋的演变以及人类活动对环境的影响, 取得了大量研究成果, 丰富了全球大陆边缘沉积的研究。相对于其他泥质区, 山东半岛近岸泥质区的研究, 特别是沉积记录承载的环境演化信息还需要进一步挖掘。
山东半岛近岸泥质区是离中国大陆最近的海洋泥质沉积区, 具有沉积厚度大、沉积速率高、沉积连续的特征, 沉积物主要来自黄河, 对其研究不仅有利于了解泥质区的沉积动力过程, 恢复黄河入海沉积物的历史演化, 对示踪黄河生态变化及人类活动也具有重要的科学意义。作者通过系统的文献整理, 对山东半岛近岸泥质区沉积过程和沉积记录等相关的科学问题进行梳理, 为山东半岛全新世泥质区的演化提供更全面的认识, 并对今后的研究方向进行了展望。
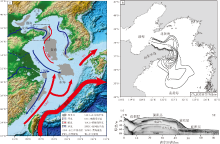 | 图 1 山东半岛全新世近岸泥质区区域背景 a— 中国东部陆架主要泥质区分布(据Wu et al., 2019, 修改), 虚线方框为山东半岛近岸泥质区; b— 山东半岛近岸泥质区等厚线图(据Yang and Liu, 2007, 修改); c— 山东半岛近岸泥质区高分辨率Chirp声呐剖面(据Yang and Liu, 2007, 修改)Fig.1 Regional background of the Holocene mud area off Shandong Peninsula |
黄河起源于青藏高原巴颜喀拉山北侧, 是世界上输沙量第二的河流, 年平均入海泥沙量约为1.1× 109t, 占全球河流输沙总量的6%(Milliman and Meade, 1983)。大多数(> 90%)的现代黄河沉积物滞留在河流水下三角洲系统(Wright et al., 2001; Wright and Friedrichs, 2006), 部分细粒沉积物随沿岸流从渤海输入到黄海, 在局部波浪、潮汐、上升流、锋面等相互作用下再悬浮并向外输送(石勇等, 2019), 在距黄河口以东约350km处周围堆积, 形成山东半岛近岸泥质区(Liu et al., 2004; Yang and Liu, 2007; 藏政晨等, 2015)。
黄海是位于太平洋西北部的半封闭边缘海, 位于中国大陆和朝鲜半岛之间, 面积约38× 104 km2, 平均水深约44m。黄海通过渤海海峡与渤海相连, 南临东海, 以山东半岛成山头和朝鲜半岛长山串联线为界分为北黄海和南黄海。黄海冬季环流主要是由黄海暖流(YSWC)、黄海沿岸流(YSCC)、山东沿岸流(SDCC)和朝鲜沿岸流(KCC)组成(图 1-a)。黄海暖流通常被认为是对马暖流(TC)的分支, 携带温暖的盐水沿黄海海槽向西北流入南黄海(图 1-a)。受东亚季风的控制, 黄海环流表现出明显的季节变化特征。
山东半岛近岸泥质区从山东半岛北部开始延伸, 绕过山东半岛的东部, 一直延伸到南黄海中部(图 1-a), 含有近400km3的沉积物, 厚度为20~40m(Liu et al., 2004; Yang and Liu, 2007)。Yang和Liu(2007)通过高分辨率浅地层剖面图发现, 山东半岛近岸泥质区的沉积模式与典型的向海推进序列和“ S” 形沉积不同, 沿岸流搬运而来的悬浮物质在陆向和海向双向跨陆架运输机制下, 形成了独特的“ Ω ” 形沉积(图 1-c), 泥质体最厚处(40m)距海岸50km, 厚度在向陆和向海方向均逐渐减小(图 1-b)。
黄海悬浮体浓度高, 水动力复杂, 季节变化明显, 是世界上悬浮体含量最高的海域之一(孙效功等, 2000)。海底沉积物的再悬浮是黄海悬浮体的主要来源。在风场、海浪以及潮流的强弱变化等控制作用下(Lu et al., 2011; Zeng et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2019), 黄海悬浮体的分布具有空间分布不均和季节性变化显著等特点(Zang et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2019)。空间上, 黄海海域悬浮体高浓度区主要位于山东半岛成山头外海、长江口外、苏北浅滩(肖合辉等, 2015); 时间上, 黄海悬浮体的分布存在显著的季节变化, 冬季悬浮体浓度可高达夏季悬浮体浓度的3倍以上(王勇智等, 2019)。此外, 沉积物的输送具有“ 夏储冬输” 的输运格局, 夏季沉积物主要沉积在河口和三角洲地区, 冬季沉积物向外海输送(杨作升等, 1992; 孙效功等, 2000; 王勇智等, 2013)。山东半岛近岸泥质区的现代沉积动力过程主要受到海洋锋面和风场的控制。
海洋锋面的空间分布和季节性变化对于该区域悬浮沉积物的输送和沉降有着重要作用(藏政晨等, 2015)。王勇智等(2013)基于冬季环流的观测和模拟, 分析了山东半岛东端外海悬浮体在强海流切变锋作用下的输送和沉积特征: 夏季悬浮体受温度锋面的约束, 悬浮体纬向的输送受到抑制; 冬季, 强海流切变锋抑制悬浮体向海的扩散。藏政晨等(2015)综合秋冬航次观测数据和HYCOM数值模拟资料, 将泥质区的形成归结为近海温度锋和近岸混合锋的共同作用。温度锋主要分布在山东半岛沿岸(图 2), 温度锋的强度和空间范围在11月份达到最大(图 2-d)。温度锋限制悬浮沉积物向海方向的移动, 混合锋面阻止悬浮沉积物朝近岸方向沉降, 沉积中心位于温度锋附近, 锋面之间的空间差异和相互作用有利于山东半岛近岸泥质区“ Ω ” 形态的发育(藏政晨等, 2015)。
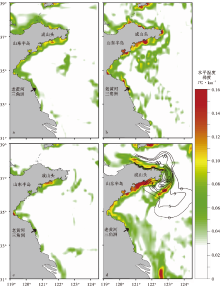 | 图 2 山东半岛近岸基于HYCOM温度场的水平温度梯度指示温度锋面位置(据Zang et al., 2017, 修改)Fig.2 Horizontal gradient of temperature based on HYCOM temperature fields indicating locations of thermal fronts off Shandong Peninsula (modified from Zang et al., 2017) a— 4月份; b— 5月份; c— 9月份; d— 11月份。d图中等值线为山东半岛近岸泥质区等厚线(m) |
Wang等(2019)建立了渤海和黄海耦合的校准模型, 对山东半岛近岸泥质区沉积物的沉积和运输过程进行研究, 发现其沉积模式与锋面的季节性变化有关。春季到秋季, 黄海冷水团周围形成的温度锋面限制了沉积物向海方向的输送, 有利于泥质区的沉积; 夏秋过渡时期, 温度锋面向海移动, 风和海浪的增强使沿海地区的悬浮沉积物浓度增加, 泥质区的沉积量最大; 冬季, 垂向混合均匀, 温跃层消失, 温度锋面减弱甚至消失, 海底再悬浮导致了更高的悬浮沉积物浓度, 沉积物向海移动, 在南黄海沉积(Wang et al., 2019)。
前人对于黄海温度锋面的研究局限于其时空分布格局及对泥质沉积体发育等方面, 而锋面长时间尺度上的时空演化及其对沉积物沉积动力过程的影响机制需要进一步研究。
 | 图 3 山东半岛近岸深度平均的悬浮沉积物浓度(SSC)和深度积分的悬浮沉积物通量(SSF)日平均分布(据Wang et al., 2020, 修改) a— 寒潮爆发阶段; b— 寒潮爆发阶段; c— 寒潮爆发阶段; d— 北风减弱阶段; e— 北风减弱阶段; f— 北风减弱阶段。图中箭头方向指的是SSF的方向, 箭头长短表明悬浮沉积物通量的大小Fig.3 Spatial distributions of daily depth-averaged SSC and the daily depth-integrated sediment flux vectors off Shandong Peninsula (modified from Wang et al., 2020) |
黄河泥沙在冬季强风作用下输送至渤海湾, 结合波浪作用, 进一步输送至黄海和山东半岛南部近海, 形成泥质区, 为山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成和演化提供了动力基础(Qiao et al., 2016)。冬季风, 特别是冬季强风, 被认为是渤海黄河源沉积物向黄海长距离输送的主要因素(Qiao et al., 2016)。山东半岛近岸泥质区北部的形成与夏季南风密切相关, 东南部则与冬季北风(尤其是强风)有关(Qiao et al., 2016)。此外, 阵发性的非典型风场(夏季偏北风或冬季偏南风)对沉积物输运以及长期输沙累积具有重要作用(Wu et al., 2019)。夏季, 主导风向的逆转(南风变为北风)使渤海和黄海水交换量增大, 但是由于夏季悬浮沉积物浓度低, 风向的逆转对泥沙运输影响有限; 冬季, 北风减弱或者风向倒转(北风变为南风), 导致大量的水从南黄海流入北黄海甚至是渤海, 先前流出渤海的沉积物随回流而返回, 有效地阻碍了渤海沉积物的输出(Wu et al., 2019)。Wang等(2020)研究发现冬季风暴期间(图 3-a, 3-b, 3-c)渤海海峡的输沙量会显著增加, 渤海海峡东向的沉积物净通量值高; 北风减弱期间(图 3-d, 3-e, 3-f)海峡内的沉积物浓度降低, 海峡的西向通量比在风暴期要小得多。这种不对称性的悬浮体通量使得风暴期间大量的沉积物沿山东半岛从渤海运输到黄海(Wang et al., 2020), 有利于山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成。
黄河物质随沿岸流从渤海进入到北黄海, 在山东半岛和辽东半岛附近沉积(石勇等, 2019), 且大部分全新世的黄河沉积物仍保存在黄海体系中(Yang and Liu, 2007), 黄河输入的沉积物被认为是黄海泥质区的主要物源。诸多学者通过矿物学、地球化学等方法对山东半岛沿岸表层沉积物源进行示踪研究(窦衍光等, 2012; 蓝先洪等, 2016; 张尧等, 2018), 证实了山东半岛近岸泥质区的物质主要来自于黄河沉积物这一观点。除黄河带来的大量沉积物之外, 近岸侵蚀以及当地小河流携带的入海物质同样给研究区贡献了一定的物源(刘金庆等, 2016)。沉积物物源的示踪增强了对黄河— 渤海— 黄海源-汇体系的理解, 为认识山东半岛沿岸泥质区的环境演化提供科学依据。
3.1.1 黏土矿物
黏土矿物是海洋沉积物中易迁移的物质, 其组成受地质背景、流域源岩、地带性气候和化学风化控制(万世明等, 2020), 对研究洋流体系演变、沉积环境变化以及物质来源输入具有重要的指示意义(Cong et al., 2021)。在黏土矿物组合中, 黄河和长江沉积物都以伊利石— 绿泥石— 高岭石— 蒙皂石为主; 而与长江沉积物相比, 黄河沉积物中伊利石含量更低、蒙皂石含量更高, 且伊利石与蒙皂石含量的比值小于6(范德江等, 2001)。研究表明, 该区域的黏土矿物主要由伊利石、蒙皂石、绿泥石和高岭石组成, 其中伊利石的含量最高(李国刚等, 2010; Qiu et al., 2014; 韩宗珠等, 2016), 伊利石与蒙皂石含量比值小于 6, 与黄河沉积物的特征值相似, 排除长江沉积物对于研究区的贡献(Qiu et al., 2014; 韩宗珠等, 2016)。在伊利石、蒙皂石、(高岭石+绿泥石)三角端元图(ISKc图)中(图 4), 研究区内黏土矿物的投点位置大多数与黄河沉积物相似, 说明沉积物主要来源于黄河。黄河型物质在山东半岛南北两侧均有分布(李国刚等, 2010)。山东半岛南岸有乳山河、大沽河、五龙河等中小型河流入黄海, 对研究区的物质组成产生一定的影响(Hu et al., 2018)。
 | 图 4 山东半岛近海表层沉积物伊利石— 蒙皂石— (高岭石+绿泥石)三角端元图(ISKc图) 黄河数据据范德江等(2001), Milliman等(1985), Ren和Shi(1986); 长江数据据范德江等(2001); 五龙河、乳山河、大沽河数据据Hu等(2018); 山东半岛近岸泥质区样品数据据韩宗珠等(2016), 李国刚等(2010), Hu等(2018), Qiu等(2014)Fig.4 Triangle endmember map of illite-smectite-(kaolinite+chlorite)in surface sediment from the Shandong Peninsula offshore |
山东半岛南岸黏土矿物组合与北岸相比明显发生变化, 矿物组合为高岭石— 伊利石— 蒙皂石— 绿泥石型或伊利石— 高岭石— 蒙皂石— 绿泥石型, 高岭石含量升高, 标志着物源组成发生变化, 这是由于半岛河流(如白沙河、五龙河等)携带山东半岛基岩风化产物入海导致而成的(李国刚等, 2010)。Hu等(2018)对山东半岛南岸楔状沉积物的沉积结构、矿物学进行分析, 认为山东半岛南部近岸泥楔的形成既有黄河的贡献, 也有当地小河流的贡献。
3.1.2 重矿物
重矿物组合可以有效地反映沉积物源、搬运途径、矿物组分分异规律等信息, 是研究沉积环境、水动力条件和气候变化等问题的主要手段(金秉福等, 2002; 陈丽蓉, 2008; 王中波等, 2012; Dong et al., 2020)。近代黄河物源沉积物的重矿物主要以云母、普通角闪石、绿帘石组合为特征, 黑云母含量最高(图 5)。在对研究区沉积物矿物组合的研究中发现, 该区域碎屑矿物含量高, 但重矿物含量很低且种类单一, 优势重矿物为普通角闪石、云母类矿物和绿帘石(张尧等, 2018), 与黄河重矿物组合特征相似。Liu等(2017a)对山东半岛南岸沉积物的研究中, 综合碎屑矿物含量、重矿物含量等主要变量进行Q型聚类分析, 将研究区划分为4个矿物区: 青岛— 崂山近岸区沉积物受海岸侵蚀影响较大, 但受河流输入影响较小; 即墨— 海阳近岸区及千里岩岛周边地区的沉积物与五龙河、乳山河和黄河密切相关; 中部地区和海阳— 乳山近岸地区沉积物具有多源性, 受黄河物质影响显著。赵利等(2014)综合分析重矿物种类、组合特征和角闪石的矿物化学特点认为, 研究区内的物质来源是山东半岛沿岸流携带的黄河源物质和山东半岛近陆架物质的风化剥蚀物及海水对海底基岩侵蚀产物。
3.2.1 主量和微量元素
地球化学研究在沉积物物源的研究中得到了广泛应用, 其中元素地球化学被认为是鉴别沉积物来源的有效方法(Marx and Kamber, 2010; Xu et al., 2011; 杨守业等, 2015; Liu et al., 2017b; 陈禹飞等, 2020)。李国刚等(2012)对山东半岛近海表层沉积物的粒度和常量元素进行研究, 表明山东半岛近海海域表层沉积物的常量元素较为稳定, 其含量和沉积物类型密切相关, 化学蚀变指数(CIA)和TiO2/Al2O3指标指示来自于黄河的沉积物主要分布于山东半岛沿岸海域, 其分布受控于海洋环流和地形特征。窦衍光等(2012)通过分析山东半岛东部海域表层沉积物常量元素、微量元素、有机碳以及碳酸盐等指标探讨了沉积物元素组成及其控制因素和物质来源, 认为山东半岛近岸和东南部沉积物主要来源于黄河, 东北部沉积物元素组成与朝鲜半岛和鸭绿江沉积物组成相似, 推测末次冰期低海平面时东北部沉积物可能来自于朝鲜半岛或鸭绿江。
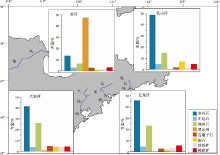 | 图 5 山东半岛近岸泥质区周边河流重矿物含量比较(数据据刘金庆等, 2016)Fig.5 Comparison of heavy mineral contents in the rivers around mud area off Shandong Peninsula (data is from Liu et al., 2016) |
3.2.2 稀土元素
山东半岛近岸泥质区沉积物的稀土元素特征表现为轻稀土元素(LREEs)富集、重稀土元素(HREEs)平坦且具有明显的Eu异常(仇建东等, 2016)。孔祥淮等(2007)对山东半岛东北部滨浅海区表层沉积物进行了稀土元素含量和粒度测试, 基于稀土元素球粒陨石标准化和上陆壳标准化配分模式、元素比值计算对比, 验证了研究区沉积物与黄河入海沉积物具有相同的源区。仇建东等(2016)对山东半岛南部滨浅海区QDZ03钻孔进行了稀土元素地球化学分析和沉积物物源研究, 通过对稀土元素配分模式、Ce-La元素的DF判别函数、LREE/HREE与REE关系分析认为, 钻孔沉积物的物源在晚更新世前后发生了变化, 在晚更新世之前, 物质来源可能是混合源或受到后期环境改造影响较大; 晚更新世之后, 沉积物主要受五龙河和黄河沉积物的影响, 尤其是2000年以后, 沉积物与黄河沉积物最为相似。Qiu等(2014)对岩心QDZ03沉积物地球化学特征分析得出, 研究区的物源与黄河典型沉积物的物源不同, 认为是黄河和山东半岛近岸沉积物共同贡献的结果。Liu等(2009)对岩心NYS-101地球化学特征分析发现, 岩心最上部的沉积物除了来自黄河沉积物外, 还有来自朝鲜半岛部分河流的沉积物和长江沉积物, 归因于全新世中期黄海和邻近地区的环流调整使得来自朝鲜半岛和长江的沉积物开始向山东半岛沿岸输送。
山东半岛全新世泥质区形成的具体时间由于受到测年材料和钻孔沉积物的限制, 还存有争议。Milliman等(1987)认为泥质体在5ka BP以后沉积。Alexander等(1991)基于水下三角洲沉积物的14C年龄推测, 楔状沉积主要形成于6200~4060a BP, 其形成与冰后期海平面的升高有关。Liu等(2001)根据碳同位素年龄、浅地层剖面图和区域海平面变化得出, 11ka左右冰后期海平面上升速度减缓, 夏季风增强导致泥质沉积体的形成。杨子赓(2004)认为其形成于7000~6000 a BP 期间。Liu等(2004)在后期的研究中认为, 在11.4 ka BP海平面上升阶段有1.8 ka的停滞期, 山东半岛楔状沉积开始形成, 发育时间为11~9.2 ka BP。基于14C年龄、浅地层剖面图和岩心沉积物特征的分析, Liu等(2007)认为该泥楔是在11.6~6.5 ka BP陆架水体逐渐加深的环境和高海平面时期下形成的。总体上, 前人的研究结果普遍认为山东半岛泥质体形成于全新世, 与末次冰期以来海平面的升降密切相关。
山东半岛近岸泥质区演化与末次盛冰期(LGM)后海平面的上升和古气候的变化密切相关(Liu et al., 2004, 2007)。末次盛冰期以来, 中国东海、黄海以及南海的海平面呈阶梯式变化: 长期的缓慢海侵被几个短且快速的洪水事件打断(图 6)。
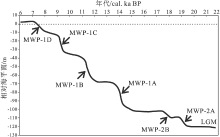 | 图 6 西太平洋(黄海、东海、南海)末次盛冰期以来海平面变化(据Liu et al., 2004, 修改) LGM: 末次盛冰期; MWP: 融水脉冲Fig.6 Sea level changes in the Western Pacific(Yellow sea, East China Sea, South China Sea)since the Last Glacial Maximum(modified from Liu et al., 2004) |
Liu等(2001, 2004)通过对北黄海高分辨率浅地层剖面的分析, 认为山东半岛近岸泥质区分为近端区和远端区: 近端区形成于11~9.2 ka之间, 是对MWP-1B事件后海平面上升缓慢和夏季风增强导致黄河向北黄海流量增加的响应; 远端区自9.2 ka开始形成, 反映了海平面的再次快速上升, 黄河口向西退移至渤海湾。Liu等(2007)依据高分辨率浅层地震剖面与钻孔NYS101和NYS102的沉积物分析, 结合海平面的变化及物源特征, 将山东半岛泥质体划分为DU1、DU2和DU3共3个沉积单元, 指出泥质体的地层层序记录了冰期海侵过程中的几个主要融水事件。沉积环境演化过程分为4个阶段: (1)末次盛冰期时整个黄海暴露于地表, 冰消期早期(13.0~11.6 cal.ka BP)海平面上升相对缓慢, 沉积环境为盐沼和潮坪环境, 沉积单元DU4开始形成(图7-a); (2)11.6~9.6 cal.ka BP, 海平面快速上升后, 末次盛冰期海侵入侵渤海, 随后海平面上升速率减慢, 黄河开始流入渤海, 来自渤海的黄河沉积物开始在河口堆积, 形成了相对较粗、向上变细的沉积单元DU3, 这一阶段沉积环境为近岸潮间带环境(图 7-b); (3)9.6~6.5 cal.ka BP, MWP-1C事件和8.2 ka冷事件导致海平面上升, 黄河向渤海的沉积物供给量增加, DU2沉积期间开始出现楔状沉积的形态, 海平面上升过程中陆架水深增大, 沉积环境由半咸水环境变为开阔的海洋沉积环境(图 7-c); (4)冰后期(6.5cal.ka BP)海侵到达高峰, 渤海和黄海及周边海域建立现代海洋环境, DU1粒度总体上呈向上变粗趋势, 此时的沉积环境为高海平面时期的陆架环境, 反映了近6500 a来黄河三角洲持续向渤海西部进积(图 7-d)。Xue等(2018)认为山东半岛近岸泥质区的演化主要受东亚冬季风强度变化和渤海的空间范围控制: 9600 cal.a BP以来泥质区一直处于累积阶段; 8200~5000cal.a BP期间, 渤海的面积较大, 强烈的东亚冬季风引发了相对强烈的落潮流, 渤海海峡南部悬浮沉积物浓度升高, 泥质区的主体快速形成; 5000 cal.a BP后, 东亚季风减弱, 泥质沉积速率减慢。
山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成过程复杂, 其沉积演化受多种因素的控制, 如黄河沉积物的供应、渤海海底全新世沉积物的海侵侵蚀和改造、全新世海平面的阶梯式上升、渤海洋流系统和潮流强度的变化、全新世早期东亚夏季风的增强、渤海黄河口的西移等(Liu et al., 2004, 2007; Yang and Liu, 2007; Xue et al., 2018)。Liu等(2004)认为此沉积体的形成受冰期后海平面上升、亚洲夏季风再加强和黄河河口摆动所控制, 将其归为复合水下三角洲体系。Liu等(2007)根据其沉积特征将其视为渤海东部潮汐沉积体系的一个远端部分。Xue等(2018)则认为山东半岛近岸泥质区实质上是渤海海峡向海侧的一个大型泥质退潮三角洲。上述研究表明, 山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成过程主要受控于末次冰期以来古气候和海平面变化, 但具体形成过程还存在争论。未来需要获取山东半岛近岸泥质区不同位置更多穿透泥质体的钻孔岩心沉积物, 获取精确的定年数据, 建立可靠的地层格架, 来约束其形成过程。
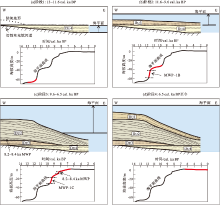 | 图 7 冰期后海平面变化与山东半岛近岸泥质区演化概念模型(据Liu et al., 2007, 修改) DU1-DU4: 沉积单元; MWP: 融水脉冲Fig.7 A conceptual model of evolution of mud area off Shandong Peninsula in relation to different stages of postglacial sea-level change(modified from Liu et al., 2007) |
东亚季风受太平洋和欧亚大陆间海陆热力差异以及青藏高原影响, 是全球大气环流的重要组成部分, 同时影响和控制着中国区域气候的变化, 对于东亚季风演化研究具有重要的意义(汪品先, 2009)。最近的几十年, 许多学者通过黄土(Ding et al., 2001; Porter, 2001)、冰心(Thompson et al., 1997; 施雅风等, 1999)、泥炭(Hong et al., 2000; Hong et al., 2001)、石笋(Dong et al., 2015; Li et al., 2018)、湖泊沉积物(Zhang et al., 2018; Lan et al., 2020)等陆相指标揭示了东亚季风的高分辨率变化。陆架泥质区具有沉积速率高、沉积连续等特点, 为东亚季风的演变研究提供了新的高分辨率载体(向荣等, 2006; Liu et al., 2018b; Dong et al., 2021)。
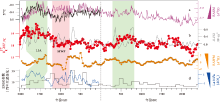 | 图 8 不同气候指标比较(据Zhang et al., 2019, 修改) a— 北半球温度(T)和石笋 δ 18O 记录的东亚夏季风(EASM); b— U37´ k记录的表层海水温度(SST)和太阳总辐射变化(△ TSI); c— δ 18O记录的东亚冬季风(EAWM); d— 南方涛动指数(SOIpr)记录的La Niñ a活动和ENSO温暖事件次数。LIA: 小冰期; MWP: 中世纪温暖期。绿色方块代表较寒冷时期, 粉色方块代表温暖时期Fig.8 Comparison of different climate indicators(modified from Zhang et al., 2019) |
山东半岛近岸泥质区所在的现代黄海环境对东亚冬季风的高纬度驱动和太平洋的低纬度驱动非常敏感, 其沉积物可以记录高分辨率的古气候信息, 为进一步追溯黄海在全新世千年和百年尺度上对不同气候事件(如太阳总辐射照度、东亚冬季风、厄尔尼诺与南方涛动、海平面变化、黑潮等)的响应提供了良好的材料(Jia et al., 2019)。
冬季, 中国东部边缘海暴露于盛行东亚冬季风下, 在东亚冬季风驱动下, 增强的沿岸流使细粒沉积物再悬浮运输到泥质区; 沉积物的粒径在强东亚冬季风作用下会变得更粗, 因此沉积物的粒度指标被广泛应用于东亚冬季风强度重建工作中(肖尚斌等, 2004; 向荣等, 2006; 徐方建等, 2009)。胡邦琦等(2012)对南黄海中部泥质区ZY-1、ZY-2、ZY-3柱样采用沉积物敏感粒度法、沉积层序法和AMS14C测年法分析, 重建了研究区中全新世(过去7200年)以来东亚冬季风的演化, 研究发现千年尺度上东亚冬季风与东亚夏季风具有相同的变化趋势, 然而在百年尺度上两者的变化趋势相反, 推测是对太阳活动减弱的反应。Tu等(2017)对中国东部近海陆架泥质区的沉积物粒度敏感组分反演的全新世东亚冬季风演化的研究进行了梳理和比较, 结果表明不同泥质区甚至同一泥质区沉积物粒度敏感组分所记录的冬季风演化趋势不同, 因此在重建冬季风的强度时应对沉积物的粒度敏感组分的指示意义进行评估。
最近研究发现, 利用U37´ k、TEX86指标重建表层海水温度(SST)可以进一步恢复全新世中晚期以来东亚冬季风在千年和百年尺度上的变化(Jia et al., 2019)。Nan等(2017)基于山东半岛近岸泥质区Z8岩心沉积物长链烯烃不饱和比值(U37´ k)的分析, 重建了3500~1300 cal.a BP的表层海水温度, 发现表层海水温度与东亚冬季风的变化规律具有一致性, 揭示了气候变化是影响黄海暖流形成和演化的关键要素。随后Chen等(2019)利用高分辨率粒度和有机碳指标(
本研究从沉积动力过程、物质来源、沉积环境及东亚冬季风的演化方面对前人的工作进行梳理。可以看出, 对山东半岛近岸泥质区的沉积过程与沉积记录研究方面已经有了深入的认识, 但是在以下方面尚需要进一步的工作:
1)山东半岛近岸泥质区的形成过程还缺乏统一认识, 需进一步加强连续现代观测、数值模拟、连续高分辨沉积记录等方面的研究, 重建山东半岛近岸泥质区动力条件和演化史。
2)普遍认为黄河沉积物是山东半岛近岸泥质区陆源物质的来源, 当地河流的输入和近岸侵蚀也会为研究区带来一定物源, 但是其在泥质体沉积过程中的定量估算还需要进一步的工作。
3)目前对于黄海高分辨率古气候记录的研究主要集中在黄海中部泥质区, 山东半岛近岸泥质区有所涉及但资料较少。山东半岛近岸泥质区古气候研究工作需要进一步加强, 包括合适指标的选取, 为东亚季风的演化提供新的证据。
4)黄河的调水调沙与改道、极端天气以及人类活动对于黄河沉积物运输的机制需加强研究, 为山东半岛近岸泥质区演化提供理论基础和动力解释。
5)山东半岛近岸泥质区在长时间尺度(末次盛冰期以来)上有机质埋藏、有机碳矿化以及相关的C-S-Fe生物地球化学过程对沉积环境演化的响应机制尚不明确。
(责任编辑 李新坡; 英文审校 徐 杰)
| 1 |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|

